Github代码仓库
spring开发服务器端 Http消息机制(也即一些编程规范)
controller一般只负责Http消息的传输;service负责业务逻辑的处理;repository负责执行数据库操作;domain层是领域模型对象,对应数据库中相应的表 controller中基本的交互方法应写成:
1 2 3 @RequestMapping("自定义的路径") @ResponseBody public Response doSomething (Request request)
所有的Http请求都会被解析为Request类的实例,而对于基本的返回类型(String、JSON之类的),则一律定义成Response类实例
基础CURD
很多框架会有比如BaseEntity,BaseDao,BaseService之类的基础类,很多新建的领域对象模型都是从这些基础类继承而来。
orm框架:hibernate和mybatis各有千秋
@RequiresAuthorization的实现 以framework-example中的StandardController为例。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @RequiresAuthorization( requestType = RequestType.QUERY, serviceClass = UserService.class, queryScope = AuthorizationScope.ALL, editScope = AuthorizationScope.ORGANIZATION, deleteScope = AuthorizationScope.ORGANIZATION) public Response queryStandards (Request request) ... }
queryStandards方法前面加上了@RequiresAuthorization注解,看一下@RequiresAuthorization的定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Documented @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface RequiresAuthorization{ RequestType requestType () ; AuthorizationScope queryScope () default AuthorizationScope.ORGANIZATION ; AuthorizationScope editScope () default AuthorizationScope.USER ; AuthorizationScope deleteScope () default AuthorizationScope.USER ; Class<? extends BaseService<? extends BaseEntity>> serviceClass(); }
当queryStandards方法执行的时候,将会触发com.sinosteel.framework.core.auth包下面的类AuthorizationAspect中的filterAuthorizations方法,AuthorizationAspect被定义为一个切面,filterAuthorizations方法作为@RequiresAuthorization注解的切入点。进入该方法内部:
1 2 3 Object arg = args[0 ]; Request request = (Request) arg; User requestUser = request.getUser();
此处获取Controller中queryStandards方法的入口参数,即一个Request,并获取request中的参数user。查看Request的类型定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Request private User user; private String uri; private String client; private String dateTime; private JSONObject params; private List<MultipartFile> files; ... }
然后将@RequireAuthorization注解中的属性值提取出来,得到requestType, serviceClass, queryScope, editScope,deleteScope。接着进行环绕处理:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 if (requestType == RequestType.QUERY) { Response response = (Response) joinPoint.proceed(args); JSON data = response.data; if (data instanceof JSONObject) { JSONObject dataJson = (JSONObject) data; JSONArray dataJsonArray = dataJson.getJSONArray("data" ); int filteredDataCount = filterData(dataJsonArray, requestUser, queryScope, editScope, deleteScope); int total = dataJson.getIntValue("total" ); dataJson.put("total" , total - filteredDataCount); } else if (data instanceof JSONArray) { JSONArray dataJsonArray = (JSONArray) data; filterData(dataJsonArray, requestUser, queryScope, editScope, deleteScope); } return response; }
上述代码首先判断请求类型为QUERY,则执行查询操作,即执行Controller中的standardService.queryStandards(request.getParams())方法,进入queryStandards方法,在com.sinosteel.metallurgical.knowledge.service.StandardService中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public JSONObject queryStandards (JSONObject params) StringBuilder hqlBuilder = new StringBuilder("FROM Standard standard WHERE 1 = 1 " ); HashMap<String, Object> paramsMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(); ... hqlBuilder.append("ORDER BY ISSUE_DATE DESC" ); Pager pager = JSONObject.toJavaObject(params.getJSONObject("pagination" ), Pager.class); PageResult<Standard> pageResult = standardRepository.executeHql(hqlBuilder.toString(), paramsMap, pager); return pageResult.toJSONObject(); }
该方法定义好查询语句后执行standardRepository.executeHql方法,即执行standardRepository的实现类standardRepositoryImpl中的executeHql方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public PageResult<T> executeHql (String hql, HashMap<String, Object> paramsMap, Pager pager) Query query = this .entityManager.createQuery(hql); setParams(query, paramsMap); setPager(query, pager); List<T> data = query.getResultList(); String countHql = this .genCountSql(hql); Query countQuery = this .entityManager.createQuery(countHql); setParams(countQuery, paramsMap); int total = Integer.parseInt(countQuery.getSingleResult().toString()); PageResult<T> queryResult = new PageResult<T>(total, data); return queryResult; }
首先设置查询变量和分页信息,其中setPager需要注意:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 private void setPager (Query query, Pager pager) if (pager != null ) { int current = pager.current; int pageSize = pager.pageSize; int firstIndex = pageSize * (current - 1 ); query.setFirstResult(firstIndex); query.setMaxResults(pageSize); } }
这里设置每页只查询pageSize条记录,根据current的不同设置查询结果集的初始位置=pageSize * (current - 1)。回到execuSql方法中,查询完得到的结果是长度为pageSize的记录,数据类型为Standard,这里用模板T表示的,泛指所有可查询类型。将查询结果数量total和data封装到PageResult中返回给StandardService中的queryStandards方法,该方法将pageResult对象转换为JSONObject后返回给Controller中的queryStandards方法,Controller中的queryStandards方法将该JSONObject封装到Response对象中返回给调用方。查看Response的类型定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class Response public ResponseType status; public JSON data; public String message; public Response () { this .status = null ; this .data = null ; this .message = null ; } public Response (ResponseType status, JSON data, String message) { this .status = status; this .data = data; this .message = message; } }
到此queryStandards方法执行完毕,返回到环绕处理阶段。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 if (requestType == RequestType.QUERY) { Response response = (Response) joinPoint.proceed(args); JSON data = response.data; if (data instanceof JSONObject) { JSONObject dataJson = (JSONObject) data; JSONArray dataJsonArray = dataJson.getJSONArray("data" ); int filteredDataCount = filterData(dataJsonArray, requestUser, queryScope, editScope, deleteScope); int total = dataJson.getIntValue("total" ); dataJson.put("total" , total - filteredDataCount); } else if (data instanceof JSONArray) { JSONArray dataJsonArray = (JSONArray) data; filterData(dataJsonArray, requestUser, queryScope, editScope, deleteScope); } return response; }
以上我们得到返回值response,获取response中的data(pageResult),获取pageResult中的data属性值(List<Standard>类型),赋值给dataJsonArray,调用filterData方法,遍历dataJsonArrary,过滤掉不满足权限控制的查询结果,并修改total的值为原结果集中的数量-过滤掉的数量,最后返回过滤后的response。
进入filterData方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 switch (queryScope){ case ALL: break ; case ORGANIZATION: if (!hasAuthorization(queryAuthorizedOrganizationIds, authorizedOrganizationIds) && !hasAuthorization(requestOrganizationIds, authorizedOrganizationIds)) { iter.remove(); filtered = true ; filteredDataCount++; } break ; case USER: if (!hasAuthorization(queryAuthorizedOrganizationIds, authorizedOrganizationIds) && !requestUserId.equals(authorizedUserId)) { iter.remove(); filtered = true ; filteredDataCount++; } break ; case NONE: iter.remove(); filtered = true ; filteredDataCount++; break ; }
如果为ORGANIZATION,则判断用户是否有查询authorizedOrganizationIds的权限以及用户是否属于authorizedOrganizationIds这个组织,如果都不满足,则将该条查询从dataJsonArrary中删除。由此完成了权限控制。
总结一下 :@RequiresAuthorization注解是通过切面来实现的,用户在浏览器访问/queryStandards时,该切面便会执行,完成权限控制。
shiro注解授权源码实现 授权流程 概括的说,shiro在实现注解授权时采用的是Spring AOP的方式。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Bean public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor (SecurityManager securityManager) AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor = new AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(); authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor.setSecurityManager(securityManager); return authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor; }
AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor继承自StaticMethodMatcherPointcutAdvisor,StaticMethodMatcherPointcutAdvisor为静态方法匹配器切点定义的切面,默认情况下,匹配所有的目标类;继承自PointcutAdvisor,代表具有切点的切面,它包含Advice和Pointcut两个类,这样我们就可以通过类、方法名以及方法方位等信息灵活地定义切面的连接点,提供更具适用性的切面。将shiro的securityManager传入AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 public class AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcutAdvisor private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor.class); private static final Class<? extends Annotation>[] AUTHZ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES = new Class[] { RequiresPermissions.class, RequiresRoles.class, RequiresUser.class, RequiresGuest.class, RequiresAuthentication.class }; protected SecurityManager securityManager = null ; public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor () **setAdvice**(new AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor()); } public SecurityManager getSecurityManager () return securityManager; } public void setSecurityManager (org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager) this .securityManager = securityManager; } public boolean matches (Method method, Class targetClass) Method m = method; if ( isAuthzAnnotationPresent(m) ) { return true ; } if ( targetClass != null ) { try { m = targetClass.getMethod(m.getName(), m.getParameterTypes()); if ( isAuthzAnnotationPresent(m) ) { return true ; } } catch (NoSuchMethodException ignored) { } } return false ; } private boolean isAuthzAnnotationPresent (Method method) for ( Class<? extends Annotation> annClass : AUTHZ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES ) { Annotation a = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, annClass); if ( a != null ) { return true ; } } return false ; } }
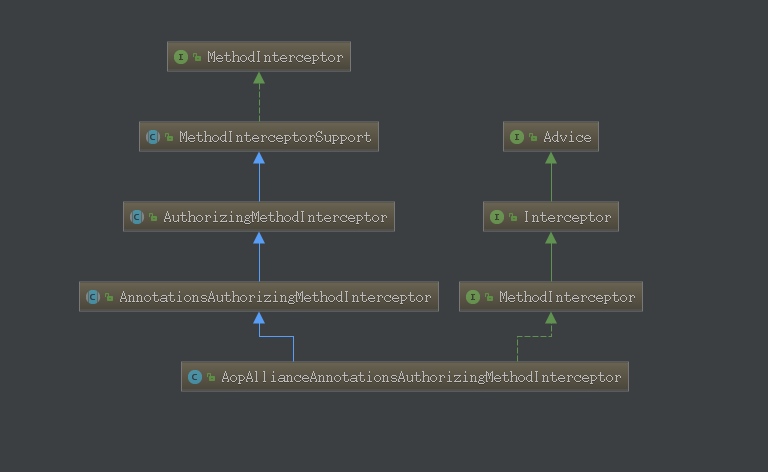
AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor类中的setAdvice方法,传入一个Advice(通知)。查看AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor的继承关系发现该类继承自org.aopalliance.aop.Advice和org.apache.shiro.aop.MethodInterceptor
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor () List<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor>(5 ); AnnotationResolver resolver = new SpringAnnotationResolver(); interceptors.add(new RoleAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver)); interceptors.add(new PermissionAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver)); interceptors.add(new AuthenticatedAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver)); interceptors.add(new UserAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver)); interceptors.add(new GuestAnnotationMethodInterceptor(resolver)); setMethodInterceptors(interceptors); }
可以看到,这里添加了5个AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor,分别对应@RequiresRoles注解权限、@RequiresPermissions注解权限、@RequiresAuthentication注解权限、@RequiresUser注解权限和@RequiresGuest注解权限。这里以@RequiresPermissions为例展开讨论。
1 2 3 public PermissionAnnotationMethodInterceptor (AnnotationResolver resolver) super ( new PermissionAnnotationHandler(), resolver); }
上面代码new一个PermissionAnnotationHandler对象。然后PermissionAnnotationHandler对象的构造器设置annotationClass = RequiresPermissions.class,如下
1 2 3 public PermissionAnnotationHandler () super (RequiresPermissions.class); }
这样PermissionAnnotationMethodInterceptor就设置好了,回到AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor方法拦截器中,代理对象的方法被调用时触发回调方法invoke(),调用父类AuthorizingMethodInterceptor的invoke()方法,如下:
1 2 3 4 public Object invoke (MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable assertAuthorized(methodInvocation); return methodInvocation.proceed(); }
在com.sinosteel.framework.config.shiro.ShiroConfig类中,定义了一个Spring IoC容器,配置了securityManager,并配置securityManager的subjectFactory(用于产生subject,setSessionCreationEnabled(false),表示不创建会话,将web应用做成无会话的),sessionManager(会话管理)和realm(就是自定义的com.sinosteel.framework.core.auth.StatelessAuthorizingRealm)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Override protected boolean onAccessDenied (ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception { String clientDigest = request.getParameter("clientDigest" ); String username = request.getParameter("username" ); StatelessAuthenticationToken token = new StatelessAuthenticationToken(username, clientDigest); try { getSubject(request, response).login(token); return true ; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); onLoginFail(response); return false ; } }
客户端在验证时,除了发送用户名和密码外,还需要发送使用基于散列的消息认证码生成的消息摘要,StatelessAccessControlFilter收到验证请求后,根据username和消息摘要生成无状态的token,并交由StatelessAuthorizingRealm进行验证。StatelessAuthorizingRealm的doGetAuthenticationInfo方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo (AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { StatelessAuthenticationToken statelessToken = (StatelessAuthenticationToken)token; String username = (String)statelessToken.getPrincipal(); JSONObject userInfoJson = CacheUtil.getUserInfoJson(username); if (userInfoJson == null ) { User user = userRepository.findByUsername(username); if (user == null ) { return null ; } userInfoJson = CacheUtil.saveUserInfoCache(user); } String serverDigest = HmacSHA256Util.digest(getKey(username), userInfoJson.getString("password" )); SimpleAuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username, serverDigest, getName()); return authenticationInfo; }
此处首先根据客户端传入的用户名获取相应的密钥,然后使用密钥对请求参数生成服务器端的消息摘要serverDigest;然后生成authenticationInfo,返回给调用方,与客户端的消息摘要进行匹配;如果匹配,说明是合法客户端传入的,则login成功;否则是非法的。